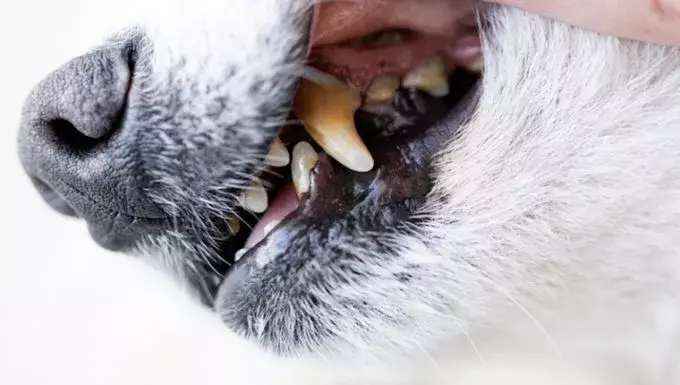
Gingival hyperplasia is a prevalent but often overlooked dental condition in canines, marked by the abnormal enlargement and inflammation of the gums. This situation can often lead to more serious issues, including periodontal disease, which can severely affect a dog’s overall health. While this condition can occur in any dog, certain breeds are particularly predisposed to developing gingival hyperplasia, often requiring pet owners to be vigilant about their pets’ oral care.
Recognizing the symptoms of gingival hyperplasia is crucial for early intervention. Typical indicators include swollen, reddened gums and noticeable thickening of the tissue. It’s important for dog owners to look out for signs such as gum bleeding, the development of pockets along the gum lines, and abnormal tissue overgrowth, which can often be mistaken for normal age-related changes. Some dogs may even engage in self-injurious behaviors, like chewing their swollen gums, exacerbating the problem and leading to further traumatic injury.
Dental plaque and bacteria are primary culprits in the onset of gingival hyperplasia. However, the condition’s emergence can be influenced by a number of factors, including genetics and certain medical treatments. Breeds such as Great Danes, Boxers, and Dalmatians are particularly susceptible, which highlights the importance of tailored dental care based on breed predispositions. Additionally, the use of immunosuppressive drugs can trigger the condition, revealing the multifaceted nature of its potential causes.
If gingival hyperplasia is suspected, a visit to the veterinarian is crucial. A thorough examination of the mouth and teeth is the first step, complemented potentially by diagnostic tools such as X-rays and biopsies. These assessments not only confirm the diagnosis but also help rule out other possible dental or systemic issues. Early diagnosis can significantly influence treatment outcomes, making routine veterinary dental checks essential for at-risk breeds.
After a diagnosis is made, treatment typically involves surgical intervention to remove excess gum tissue and clean any pockets that have formed. This procedure is vital in restoring gum health and preventing the recurrence of the condition. Pain management, along with diligent post-operative care, is essential in ensuring the dog’s comfort during recovery. Alongside surgical treatment, veterinarians often recommend a customized dental care routine. Regular teeth cleanings and home dental hygiene practices play a crucial role in preventing gingivitis and more complicated periodontal diseases.
Gingival hyperplasia should not be underestimated or dismissed as a minor issue. Pet owners have a responsibility to monitor their dogs’ oral health closely and consult with veterinarians at the first sign of trouble. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective treatments for this condition can lead to improved quality of life for our furry companions. By being proactive and informed, pet owners can protect their beloved dogs from the painful consequences of neglected dental care.